Product Description
Special structures working principles,suitable for operation in chemical industry,oil industry,food industry,electrical utility industry,pharmacy industry,textile industry and paper making industry,etc. The other industries that need vacuum drying,concentration,distilling,dehydration and filtering also need the water-ring vacuum pump. It can be use as a backing pump of Roots Pump.
VP roots vacuum pump is in the 50 Torr-micron high vacuum range has a large pumping speed and low cost of equipment, it can be combined with various vacuum pump consists of a vacuum unit. KMBD roots vacuum pump with 5 point bearing design unique, sealing the 5 bit machine, sealing double sealing structure + mechanical seal for maze, can realize non leakage, reduce maintenance and repair of the link, ensure the roots pump and durable. Synchronous helical gear and mounted on the driving end, both to ensure quiet and reliable operation, and can reduce the load of the rotor torque. Impeller and shaft integrally cast, can provide large size shaft, impeller and reduce the risk of damage. All contact with the sealing surface of the shaft end faces are polished to reduce wear and reduce the risk of leakage, high temperature high pressure casing, and double tank design, a variety of material selection, further to ensure that the use of the user in various working conditions. Typical application: chemical, petrochemical, plastics, semiconductors, wood mixture, food processing, vacuum furnace, vacuum booster system, vacuum drying, vacuum dewatering, vacuum packaging
| Model | Capacity | Ultimate Pressure | Power | speed |
| L/S | Pa | KW | RPM | |
| VP200 | 200 | 0.05 | 4 | 2900 |
| VP600 | 600 | 0.05 | 7.5 | 2900 |
About HangZhou Ever-power group(HZPT):
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: Our group consists in 3 factories and 2 abroad sales corporations.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: How long is your delivery time ? What is your terms of payment ?
A: Generally it is 40-45 days. The time may vary depending on the product and the level of customization. For standard products, the payment is: 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.
Q: What is the exact MOQ or price for your product ?
A: As an OEM company, we can provide and adapt our products to a wide range of needs.Thus, MOQ and price may greatly vary with size, material and further specifications; For instance, costly products or standard products will usually have a lower MOQ.
Please contact us with all relevant details to get the most accurate quotation.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Custom |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Agricultural Products Processing, Farmland Infrastructure |
| Material: | Custom |
| Power Source: | Custom |
| Weight: | Custom |
| After-sales Service: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
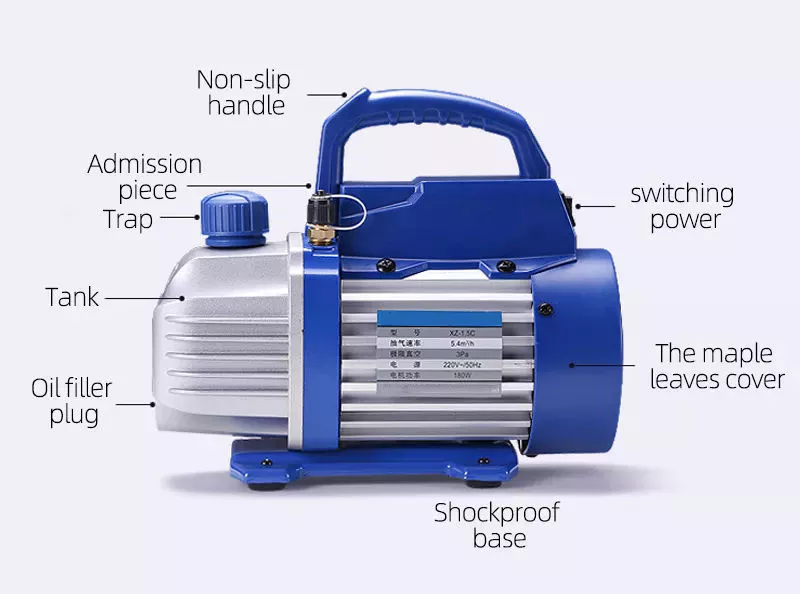
Basic knowledge of vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume and maintains a partial vacuum. Its main job is to create a relative vacuum within a given volume or volumes. There are many types of vacuum pumps. This article will describe how they work, their types, and their applications.
How it works
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device that removes gas from a system by applying it to a higher pressure than the surrounding atmosphere. The working principle of the vacuum pump is based on the principle of gas transfer and entrapment. Vacuum pumps can be classified according to their vacuum level and the number of molecules that can be removed per cubic centimeter of space. In medium to high vacuum, viscous flow occurs when gas molecules collide with each other. Increasing the vacuum causes molecular or transitional flow.
A vacuum pump has several components that make it a versatile tool. One of the main components is the motor, which consists of a rotor and a stator. The rotor and stator contain coils that generate a magnetic field when excited. Both parts must be mounted on a base that supports the weight of the pump. There is also an oil drain that circulates oil throughout the system for lubrication and cooling purposes.
Another type of vacuum pump is the liquid ring vacuum pump. It works by positioning the impeller above or below the blades. Liquid ring pumps can also adjust the speed of the impeller. However, if you plan to use this type of pump, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
Vacuum pumps work by moving gas molecules to areas of higher or lower pressure. As the pressure decreases, the removal of the molecules becomes more difficult. Industrial vacuum systems require pumps capable of operating in the 1 to 10-6 Torr range.
Type
There are different types of vacuum pumps. They are used in many different applications, such as laboratories. The main purpose of these pumps is to remove air or gas molecules from the vacuum chamber. Different types of pumps use different techniques to achieve this. Some types of pumps use positive displacement, while others use liquid ring, molecular transfer, and entrapment techniques.
Some of these pumps are used in industrial processes, including making vacuum tubes, CRTs, electric lights, and semiconductor processing. They are also used in motor vehicles to power hydraulic components and aircraft. The gyroscope is usually controlled by these pumps. In some cases, they are also used in medical settings.
How a vacuum pump works depends on the type of gas being pumped. There are three main types: positive displacement, negative displacement, and momentum transfer. Depending on the type of lubrication, these principles can be further divided into different types of pumps. For example, dry vacuum pumps are less sensitive to gases and vapors.
Another type of vacuum pump is called a rotary vane pump. This type of pump has two main components, the rotor and the vacuum chamber. These pumps work by rotating moving parts against the pump casing. The mating surfaces of rotary pumps are designed with very small clearances to prevent fluid leakage to the low pressure side. They are suitable for vacuum applications requiring low pulsation and high continuous flow. However, they are not suitable for use with grinding media.
There are many types of vacuum pumps and it is important to choose the right one for your application. The type of pump depends on the needs and purpose of the system. The larger ones can work continuously, and the smaller ones are more suitable for intermittent use. 
Apply
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industrial and scientific processes. For example, they are used in the production of vacuum tubes, CRTs, and electric lamps. They are also used in semiconductor processing. Vacuum pumps are also used as mechanical supports for other equipment. For example, there may be multiple vacuum pumps on the engine of a motor vehicle that powers the hydraulic components of an aircraft. In addition, they are often used in fusion research.
The most common type of vacuum pump used in the laboratory is the rotary vane pump. It works by directing airflow through a series of rotating blades in a circular housing. As the blades pass through the casing, they remove gas from the cavity and create a vacuum. Rotary pumps are usually single or double-stage and can handle pressures between 10 and 6 bar. It also has a high pumping speed.
Vacuum pumps are also used to fabricate solar cells on wafers. This involves a range of processes including doping, diffusion, dry etching, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and bulk powder generation. These applications depend on the type of vacuum pump used in the process, and the vacuum pump chosen should be designed for the environment.
While there are several types of vacuum pumps available, their basic working principles remain the same. Each has different functions and capacities, depending on the type of vacuum. Generally divided into positive displacement pump, rotary vane pump, liquid ring pump, and molecular delivery pump.
Maintenance
The party responsible for general maintenance and repairs is the Principal Investigator (PI). Agknxs must be followed and approved by the PI and other relevant laboratory personnel. The Agknx provides guidelines for routine maintenance of vacuum pump equipment. Agknxs are not intended to replace detailed routine inspections of vacuum pump equipment, which should be performed by certified/qualified service personnel. If the device fails, the user should contact PI or RP for assistance.
First, check the vacuum pump for any loose parts. Make sure the inlet and outlet pressure gauges are open. When the proper pressure is shown, open the gate valve. Also, check the vacuum pump head and flow. Flow and head should be within the range indicated on the label. Bearing temperature should be within 35°F and maximum temperature should not exceed 80°F. The vacuum pump bushing should be replaced when it is severely worn.
If the vacuum pump has experienced several abnormal operating conditions, a performance test should be performed. Results should be compared to reference values to identify abnormalities. To avoid premature pump failure, a systematic approach to predictive maintenance is essential. This is a relatively new area in the semiconductor industry, but leading semiconductor companies and major vacuum pump suppliers have yet to develop a consistent approach.
A simplified pump-down test method is proposed to evaluate the performance of vacuum pumps. The method includes simulated aeration field tests and four pump performance indicators. Performance metrics are evaluated under gas-loaded, idle, and gas-load-dependent test conditions.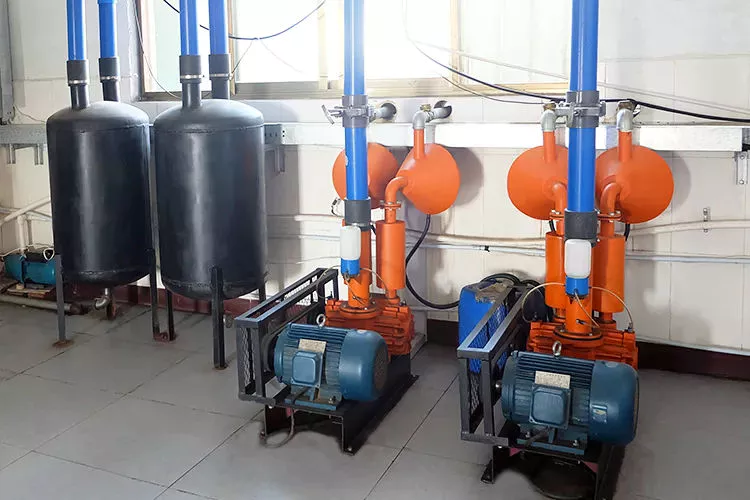 
Cost
The total cost of a vacuum pump consists of two main components: the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. The latter is the most expensive component, as it consumes about four to five times the initial investment. Therefore, choosing a more energy-efficient model is a good way to reduce the total system cost and payback period.
The initial cost of a vacuum pump is about $786. Oil-lubricated rotary vane pumps are the cheapest, while oil-free rotary vane pumps are slightly more expensive. Non-contact pumps also cost slightly more. The cost of a vacuum pump is not high, but it is a factor that needs careful consideration.
When choosing a vacuum pump, it is important to consider the type of gas being pumped. Some pumps are only suitable for pumping air, while others are designed to pump helium. Oil-free air has a different pumping rate profile than air. Therefore, you need to consider the characteristics of the medium to ensure that the pump meets your requirements. The cost of a vacuum pump can be much higher than the purchase price, as the daily running and maintenance costs can be much higher.
Lubricated vacuum pumps tend to be more durable and less expensive, but they may require more maintenance. Maintenance costs will depend on the type of gas that needs to be pumped. Lighter gases need to be pumped slowly, while heavier gases need to be pumped faster. The maintenance level of a vacuum pump also depends on how often it needs to be lubricated.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps require regular maintenance and oil changes. The oil in the diaphragm pump should be changed every 3000 hours of use. The pump is also resistant to chemicals and corrosion. Therefore, it can be used in acidic and viscous products.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China supplier Oligomer Reaction Used Discharge Melt Gear Pump vacuum pump booster
Product Description
Oligomer Reaction Used Discharge Melt Gear Pump
Specifications
1,polymer melt gear pump
2, fit for large capacity output
3, fit for very high or low viscosity polymer
Large flow rate polymer melt gear pump for reactor as discharge pump
GM-LK series of polymer melt gear pump is designed with a large entrance , suitable for the high temperature and high viscosity polymer melt conveying reaction, such as resin, chemical fiber industry, generally installed on the lower part of the reaction kettle, used as discharge pump.This series of melt gear pump has good self-priming performance, can be used in the vacuum reaction condition, the polymer material conveying and pressurization.
This GM-LK series large flow rate polymer melt gear pump used under the reaction kettle/reactor as a discharge pump, you can see the following pictures
Main application fields:
For Processing:
PET PBT
PA6 PA66 PA12
LDPE LLDPE HDPE HMWPE
PP EVA PB
PS HIPS ABS SAN
PC PEK
PMMA POM TPU
Other high viscosity Polymers
Pictures of the discharge pump for reaction kettles /reactor
The characteristic of this GM-LK series polymer melt gear pump under the reaction kettle as discharge pump.
1)it can be used on high temperature (350ºC),high pressure(15MPa),high viscosity (40,000Pas)working condition.
2)The pressure flow pulsation is very small, and even can achieve linear output flow,easy to control
3)Good self-priming performance, can be used in the entrance with the operation condition of vacuum (0.05 ~ 0.09 MPa)
4)Precise structure, high precision, long service life
Technical data:
Viscosity: 500~40000Pas(500,000~40,000,000cP)
Suction side pressure : Vacuum(-0.05~-0.09MPa)~10MPa
Discharge side pressure: 0~15MPa
Differential pressure: 15MPa
Temperature: ≤350ºC
Heating method: Fully heating medium Jacketed
HT medium pressure: ≤1.6MPa
Pump type and parameter
| Type |
Volume (cc/r) |
Max roate speed (r/min) |
Outlet pressure (MPa) |
Inlet pressure (MPa) |
Rate of flow m3/h | Temperature | ||
| Low viscosity material 1-1000Pa·s |
High viscosity material 1000~8000Pa·s |
Ultra-high viscosity material >=8000Pa·s |
||||||
| GM-LK-100 | 100 | 100 | ≤35 | Vacuum~5.0 | ≤0.51 | ≤0.36 | ≤0.21 | ≤350ºC |
| GM-LK-160 | 160 | 100 | ≤0.82 | ≤0.57 | ≤0.34 | |||
| GM-LK-200 | 200 | 100 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.7 | ≤0.4 | |||
| GM-LK-250 | 250 | 100 | ≤1.3 | ≤0.9 | ≤0.5 | |||
| GM-LK-355 | 315 | 100 | ≤1.6 | ≤1.1 | ≤0.7 | |||
| GM-LK-500 | 500 | 100 | ≤2.6 | ≤1.8 | ≤1.1 | |||
| GM-LK-750 | 750 | 80 | ≤3.1 | ≤2.1 | ≤1.3 | |||
| GM-LK-1250 | 1000 | 80 | ≤4.1 | ≤2.9 | ≤1.7 | |||
| GM-LK-2000 | 2500 | 80 | ≤10 | ≤7 | ≤4 | |||
| GM-LK-3150 | 3150 | 80 | ≤13 | ≤9 | ≤5 | |||
| GM-LK-4500 | 4500 | 60 | ≤14 | ≤10 | ≤6 | |||
| GM-LK-6300 | 6300 | 60 | ≤19 | ≤13 | ≤8 | |||
| GM-LK-8000 | 8000 | 60 | ≤24 | ≤17 | ≤10 | |||
| GM-LK-12000 | 12000 | 50 | ≤31 | ≤21 | ≤13 | |||
| GM-LK-25000 | 25000 | 50 | ≤64 | ≤45 | ≤27 | |||
| Remark:the melt gear pump flow is associated with the work speed, material viscosity, pressure, So the model selection please ask for us. |
||||||||
Sealing structure
1)the melt dynamic seal and packing seal
2)Single/double side machanical seal
3)With cooling melt dynamic seal
4)High temperature resistant packing seal
Installation way: GM-LK series melt gear pump generaaly is installed under the reaction kettle, it is used as the material discharge pump, usually arranged horizontally.
Drive mode:motor + reducer + universal coupling
Commissioning
We provide the operation manual for customers to gudie to install the screen changer, and at the requirement of user, salers should send technician to install and commissioning the die at site of Buyers, expenses of the trip should be borne by Buyers.
After-sales service
12 months with proper operation by user, all the spare parts shall be replaced free of charge under guarantee period, fee for transportation and packing will be borne by users.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Mesh Form: | External Engaged |
|---|---|
| Tooth Flank: | Skew Tooth |
| Power: | Electric |
| Type: | Normal Line Gear Pump |
| Applications: | Thermoplastic Transportation |
| Certification: | CE |

How Do You Maintain and Troubleshoot Vacuum Pumps?
Maintaining and troubleshooting vacuum pumps is essential to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Maintenance of Vacuum Pumps:
1. Regular Inspection: Perform regular visual inspections of the pump to check for any signs of damage, leaks, or abnormal wear. Inspect the motor, belts, couplings, and other components for proper alignment and condition.
2. Lubrication: Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication. Some vacuum pumps require regular oil changes or lubrication of moving parts. Ensure that the correct type and amount of lubricant are used.
3. Oil Level Check: Monitor the oil level in oil-sealed pumps and maintain it within the recommended range. Add or replace oil as necessary, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
4. Filter Maintenance: Clean or replace filters regularly to prevent clogging and ensure proper airflow. Clogged filters can impair pump performance and increase energy consumption.
5. Cooling System: If the vacuum pump has a cooling system, inspect it regularly for cleanliness and proper functioning. Clean or replace cooling components as needed to prevent overheating.
6. Seals and Gaskets: Check the seals and gaskets for signs of wear or leakage. Replace any damaged or worn seals promptly to maintain airtightness.
7. Valve Maintenance: If the vacuum pump includes valves, inspect and clean them regularly to ensure proper operation and prevent blockages.
8. Vibration and Noise: Monitor the pump for excessive vibration or unusual noise, which may indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or other mechanical issues. Address these issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Troubleshooting Vacuum Pump Problems:
1. Insufficient Vacuum Level: If the pump is not achieving the desired vacuum level, check for leaks in the system, improper sealing, or worn-out seals. Inspect valves, connections, and seals for leaks and repair or replace as needed.
2. Poor Performance: If the pump is not providing adequate performance, check for clogged filters, insufficient lubrication, or worn-out components. Clean or replace filters, ensure proper lubrication, and replace worn parts as necessary.
3. Overheating: If the pump is overheating, check the cooling system for blockages or insufficient airflow. Clean or replace cooling components and ensure proper ventilation around the pump.
4. Excessive Noise or Vibration: Excessive noise or vibration may indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or other mechanical issues. Inspect and repair or replace damaged or worn parts. Ensure proper alignment and balance of rotating components.
5. Motor Issues: If the pump motor fails to start or operates erratically, check the power supply, electrical connections, and motor components. Test the motor using appropriate electrical testing equipment and consult an electrician or motor specialist if necessary.
6. Excessive Oil Consumption: If the pump is consuming oil at a high rate, check for leaks or other issues that may be causing oil loss. Inspect seals, gaskets, and connections for leaks and repair as needed.
7. Abnormal Odors: Unusual odors, such as a burning smell, may indicate overheating or other mechanical problems. Address the issue promptly and consult a technician if necessary.
8. Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance and troubleshooting specific to your vacuum pump model. Follow the prescribed maintenance schedule and seek professional assistance when needed.
By following proper maintenance procedures and promptly addressing any troubleshooting issues, you can ensure the reliable operation and longevity of your vacuum pump.
How Do Vacuum Pumps Impact the Quality of 3D Printing?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in improving the quality and performance of 3D printing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various aspects of 3D printing to enhance the overall quality, accuracy, and reliability of printed parts. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps impact 3D printing:
1. Material Handling and Filtration: Vacuum pumps are used in 3D printing systems to handle and control the flow of materials. They create the necessary suction force to transport powdered materials, such as polymers or metal powders, from storage containers to the printing chamber. Vacuum systems also assist in filtering and removing unwanted particles or impurities from the material, ensuring the purity and consistency of the feedstock. This helps to prevent clogging or contamination issues during the printing process.
2. Build Plate Adhesion: Proper adhesion of the printed object to the build plate is crucial for achieving dimensional accuracy and preventing warping or detachment during the printing process. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum environment or suction force that securely holds the build plate and ensures firm adhesion between the first layer of the printed object and the build surface. This promotes stability and minimizes the risk of layer shifting or deformation during the printing process.
3. Material Drying: Many 3D printing materials, such as filament or powdered polymers, can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. Moisture-contaminated materials can lead to poor print quality, reduced mechanical properties, or defects in the printed parts. Vacuum pumps with integrated drying capabilities can be employed to create a low-pressure environment, effectively removing moisture from the materials before they are used in the printing process. This ensures the dryness and quality of the materials, resulting in improved print outcomes.
4. Resin Handling in Stereolithography (SLA): In SLA 3D printing, a liquid resin is selectively cured using light sources to create the desired object. Vacuum pumps are utilized to facilitate the resin handling process. They can be employed to degas or remove air bubbles from the liquid resin, ensuring a smooth and bubble-free flow during material dispensing. This helps to prevent defects and imperfections caused by trapped air or bubbles in the final printed part.
5. Enclosure Pressure Control: Some 3D printing processes, such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or binder jetting, require the printing chamber to be maintained at a specific pressure or controlled atmosphere. Vacuum pumps are used to create a controlled low-pressure or vacuum environment within the printing chamber, enabling precise pressure regulation and maintaining the desired conditions for optimal printing results. This control over the printing environment helps to prevent oxidation, improve material flow, and enhance the quality and consistency of printed parts.
6. Post-Processing and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps can also aid in post-processing steps and cleaning of 3D printed parts. For instance, in processes like support material removal or surface finishing, vacuum systems can assist in the removal of residual support structures or excess powder from printed objects. They can also be employed in vacuum-based cleaning methods, such as vapor smoothing, to achieve smoother surface finishes and enhance the aesthetics of the printed parts.
7. System Maintenance and Filtration: Vacuum pumps used in 3D printing systems require regular maintenance and proper filtration to ensure their efficient and reliable operation. Effective filtration systems within the vacuum pumps help to remove any contaminants or particles generated during printing, preventing their circulation and potential deposition on the printed parts. This helps to maintain the cleanliness of the printing environment and minimize the risk of defects or impurities in the final printed objects.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the quality of 3D printing. They contribute to material handling and filtration, build plate adhesion, material drying, resin handling in SLA, enclosure pressure control, post-processing and cleaning, as well as system maintenance and filtration. By utilizing vacuum pumps in these critical areas, 3D printing processes can achieve improved accuracy, dimensional stability, material quality, and overall print quality.

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
– Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
– Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
– Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
– Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
– Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
– Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
– Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
– Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
– Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
– Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
– Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
– Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
– Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
– Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient’s body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
– Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
– Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
– Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
– Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by Dream 2024-05-08
China Good quality Centrifugal Japanese Dump Hydraulic Kp1403A for Gear Pump Truck Auto External Vacuum vacuum pump connector
Product Description
XIXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. CHINAMFG INDUSTRY & TRADING CO., LTD.is located in the new rising port city in Chinese CHINAMFG coastline,
1 of the 16 most dynamic cities of yangtze River CHINAMFG Economic Zone—-Xihu (West Lake) Dis. County,HangZhou City,ZHangZhoug Province.
FENGHU is a company specializing in the production of hydraulic hoist, gear pump and hydro-cylinder.It’s hydraulic hoist and gear pump of KP series are sold well in more than a dozen countries and regions in Malaysia,Thailand, Indonesia and the Middle East.And we have a powerful team in the independent research,development and production of the lifting frame and gear pump. We uphold the idea of “eeping for good credit,performing for technological innovation,seeking for excellent quality and fovusing on customers’demand” as our principle.On the basis of customers’Views,we insist on quality-improvement and high-priority-product development,depending on the technology innovatuon. Beyond the voice of customer,FENGHU perseveres in providing the highest-quality product adn the best sevice.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Warranty: | 6 Month |
|---|---|
| Mesh Form: | External Engaged |
| Tooth Flank: | Straight Tooth |
| Tooth Curve: | Cycloid |
| Power: | Hydraulic |
| Type: | Normal Line Gear Pump |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Vacuum Level and How Is It Measured in Vacuum Pumps?
The vacuum level refers to the degree of pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It indicates the level of “emptiness” or the absence of gas molecules in the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of vacuum level measurement in vacuum pumps:
Vacuum level is typically measured using pressure units that represent the difference between the pressure in the vacuum system and atmospheric pressure. The most common unit of measurement for vacuum level is the Pascal (Pa), which is the SI unit. Other commonly used units include Torr, millibar (mbar), and inches of mercury (inHg).
Vacuum pumps are equipped with pressure sensors or gauges that measure the pressure within the vacuum system. These gauges are specifically designed to measure the low pressures encountered in vacuum applications. There are several types of pressure gauges used for measuring vacuum levels:
1. Pirani Gauge: Pirani gauges operate based on the thermal conductivity of gases. They consist of a heated element exposed to the vacuum environment. As gas molecules collide with the heated element, they transfer heat away, causing a change in temperature. By measuring the change in temperature, the pressure can be inferred, allowing the determination of the vacuum level.
2. Thermocouple Gauge: Thermocouple gauges utilize the thermal conductivity of gases similar to Pirani gauges. They consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined together, forming a thermocouple. As gas molecules collide with the thermocouple, they cause a temperature difference between the wires, generating a voltage. The voltage is proportional to the pressure and can be calibrated to provide a reading of the vacuum level.
3. Capacitance Manometer: Capacitance manometers measure pressure by detecting the change in capacitance between two electrodes caused by the deflection of a flexible diaphragm. As the pressure in the vacuum system changes, the diaphragm moves, altering the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
4. Ionization Gauge: Ionization gauges operate by ionizing gas molecules in the vacuum system and measuring the resulting electrical current. The ion current is proportional to the pressure, allowing the determination of the vacuum level. There are different types of ionization gauges, such as hot cathode, cold cathode, and Bayard-Alpert gauges.
5. Baratron Gauge: Baratron gauges utilize the principle of capacitance manometry but with a different design. They consist of a pressure-sensing diaphragm separated by a small gap from a reference electrode. The pressure difference between the vacuum system and the reference electrode causes the diaphragm to deflect, changing the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may have different pressure ranges and may require specific pressure gauges suitable for their operating conditions. Additionally, vacuum pumps are often equipped with multiple gauges to provide information about the pressure at different stages of the pumping process or in different parts of the system.
In summary, vacuum level refers to the pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It is measured using pressure gauges specifically designed for low-pressure environments. Common types of pressure gauges used in vacuum pumps include Pirani gauges, thermocouple gauges, capacitance manometers, ionization gauges, and Baratron gauges.
\
What Is the Difference Between Dry and Wet Vacuum Pumps?
Dry and wet vacuum pumps are two distinct types of pumps that differ in their operating principles and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between them:
Dry Vacuum Pumps:
Dry vacuum pumps operate without the use of any lubricating fluid or sealing water in the pumping chamber. They rely on non-contact mechanisms to create a vacuum. Some common types of dry vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Pumps: Rotary vane pumps consist of a rotor with vanes that slide in and out of slots in the rotor. The rotation of the rotor creates chambers that expand and contract, allowing the gas to be pumped. The vanes and the housing are designed to create a seal, preventing gas from flowing back into the pump. Rotary vane pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical applications, and industrial processes where a medium vacuum level is required.
2. Dry Screw Pumps: Dry screw pumps use two or more intermeshing screws to compress and transport gas. As the screws rotate, the gas is trapped between the threads and transported from the suction side to the discharge side. Dry screw pumps are known for their high pumping speeds, low noise levels, and ability to handle various gases. They are used in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and vacuum distillation.
3. Claw Pumps: Claw pumps use two rotors with claw-shaped lobes that rotate in opposite directions. The rotation creates a series of expanding and contracting chambers, enabling gas capture and pumping. Claw pumps are known for their oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and suitability for handling dry and clean gases. They are commonly used in applications such as automotive manufacturing, food packaging, and environmental technology.
Wet Vacuum Pumps:
Wet vacuum pumps, also known as liquid ring pumps, operate by using a liquid, typically water, to create a seal and generate a vacuum. The liquid ring serves as both the sealing medium and the working fluid. Wet vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where a higher level of vacuum is required or when handling corrosive gases. Some key features of wet vacuum pumps include:
1. Liquid Ring Pumps: Liquid ring pumps feature an impeller with blades that rotate eccentrically within a cylindrical casing. As the impeller rotates, the liquid forms a ring against the casing due to centrifugal force. The liquid ring creates a seal, and as the impeller spins, the volume of the gas chamber decreases, leading to the compression and discharge of gas. Liquid ring pumps are known for their ability to handle wet and corrosive gases, making them suitable for applications such as chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment.
2. Water Jet Pumps: Water jet pumps utilize a jet of high-velocity water to create a vacuum. The water jet entrains gases, and the mixture is then separated in a venturi section, where the water is recirculated, and the gases are discharged. Water jet pumps are commonly used in laboratories and applications where a moderate vacuum level is required.
The main differences between dry and wet vacuum pumps can be summarized as follows:
1. Operating Principle: Dry vacuum pumps operate without the need for any sealing fluid, while wet vacuum pumps utilize a liquid ring or water as a sealing and working medium.
2. Lubrication: Dry vacuum pumps do not require lubrication since there is no contact between moving parts, whereas wet vacuum pumps require the presence of a liquid for sealing and lubrication.
3. Applications: Dry vacuum pumps are suitable for applications where a medium vacuum level is required, and oil-free operation is desired. They are commonly used in laboratories, medical settings, and various industrial processes. Wet vacuum pumps, on the other hand, are used when a higher vacuum level is needed or when handling corrosive gases. They find applications in chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment, among others.
It’s important to note that the selection of a vacuum pump depends on specific requirements such as desired vacuum level, gas compatibility, operating conditions, and the nature of the application.
In summary, the primary distinction between dry and wet vacuum pumps lies in their operating principles, lubrication requirements, and applications. Dry vacuum pumps operate without any lubricating fluid, while wet vacuum pumps rely on a liquid ring or water for sealing and lubrication. The choice between dry and wet vacuum pumps depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired vacuum level.

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China high quality Stainless Steel Two Stage Vacuum Pump Lobe Rotary Piston Pump Gear Rotary Oil Pump with Moving Wheel Cart with Best Sales
Product Description
21 Years Of Experience. 3-7 days delivery, 3 Years Warranty , Reasonable Price And Best Service, CE Certificated Products. Advanced Technology. Please contact us for the offer.
Product Description
Description:
Rotary lobe pumps are positive-displacement type pumps that use 2 or more lobes rotating around parallel shafts in the pump’s body to move liquids. They are widely used in the hygienic processing industries, including food & beverage processing and biopharmaceutical manufacturing.
Working Principle of Rotary Lobe Pump:
The rotary lobe pumps, we also called them lobe rotor pumps. They are 1 popular transfer pump to conveying the food, beverage, pulp and paper, chemical, pharmaceutical and so on. The rotor lobe pump relies on 2 synchronously rotating rotors that generate suction (vacuum) at the inlet during the rotation. Thereby sucking in the material to be conveyed. Both rotors split the rotor chamber into different spaces. Then operate in the order of 1-2-3-4. The medium is delivered to the discharge port. In this cycle, the medium (material) is continuously transported out by the source.
Different Kind of Lobe Options for the Rotor Lobe Pump
1. Single Lobed Rotor: More suitable for conveying media which containing large granular materials. The breaking rate of large granular materials is low. But on other hand it is not popular 1 for used, Because its pulsation is large and pressure is low, also the volume is small for the space of transferred materials.
2. Two-Lobed Rotor (Butterfly Rotor) More suitable for conveying media which containing small and medium-size granular materials. The breaking rate to these materials is low and getting slightly pulsating. The volume is a little less than the three-lobed rotor for the space of transferred materials.
3. Three-Lobed Rotor It is widely used in 1 rotor. The volume is bigger than other type of rotors for the space of transferred materials. Also, each performance is higher than other rotors. Just, it has a certain rate of breakage to the particulate materials on the transport way.
4. Multi-Lobed Rotor(4-12) The volume is smaller for the space of transferred materials and breaking rate higher when the quantity of rotary vane of rotor be increased, Just the transport way more stable.
Character:
1,There Is A Certain Gap Between Rotor And Rotor, No Friction Coefficient, So Pump Have A Long Service Life Time.
2, It Is Easy To Install And Disassemble, And It Is Convenient To Maintain, clean . There Is Less Wearing Parts.
3, High Efficiency And Energy Saving, Stable Transportation, Low Failure Rate, No Leak Sealing And Low Noise.
4, The Viscosity Of The Transportable Medium Is, ≤2000000 CP, And The Pump Can Transfer Slurry Containing 70% Solids.
5, It Can Transport Gas, Liquid And CHINAMFG Three-Phase Mixture Materials.
6, With FD, The Flow Can Be Adjusted At Will, And The Pump Can Be Used As A General Metering Pump.
7, If you need, We Can Do The Pump With Heating Jacket.
8, Applicable Temperature: -50 °C, -250 °C.
9, Types Of Inlet/Outlet Connection: Flange Joint, Threaded Connection; Quick Connection.
10,Seal Type: Mechanical Seal And Packing Seal.
Lobe Pump Scope Of Application.
Dairy Products: Yogurt, Cream, Ice Cream, Cheese And Whey.
Beverages: Beer, Wort, Yeast, Soft Drinks, Fruit Concentrates, Fruit Drinks.
Food: Tomato Sauce, Vegetable Paste, Seasoning, Sweeteners, Yeast Paste, Salad, Meat Emulsion, Edible Oil.
Candy: Syrup, Cream Stuffing, Fruit Purée, Fruit Filling, Pudding, Jam, Jelly, Chocolate.
Cosmetics: Creams And Lotions, Hair Gels, Hair Dyes, Essential Oils.
Drugs: Pill, Extract, Emulsion, Paste.
Chemicals: Fats, Solvents, Resins And Polymers, dyes…
ADVANTAGES OF ROTARY LOBE PUMPS
Since the pump’s lobes do not come into contact with each other, lobe pumps can move solids suspended in slurries (such as cherries or olives in food processing applications) without product damage. The gentle pump action further minimizes product degradation. Can handle larger sized particles than may be pumped with other types of positive displacement pumps. It may be easily cleaned using either clean-in-place (CIP) or steam-in-place (SIP) methods, making them ideal for hygienic processing applications. Highly efficient for pumping very viscous liquids. Offer accurate and consistent fluid output that is unaffected by changes in head pressure, assuming sufficient fluid viscosity. The fluid flow can be increased or decreased by controlling the drive speed. If wetted, rotary lobe pumps are also self-priming, and can run dry for long periods of time (assuming the pump’s seals are lubricated). Generally easy to maintain.
|
Product Name: |
Sanitary Stainless Steel Rotor Rotary Lobe Pump |
|
Description: |
Designed according to 3A standard, widely used for transfer viscous media in the food-processing, cosemtics and pharmaceutical |
|
Construction: |
Horizontal Ace series, diffirent rotor shapes(single rotro,tri-lobe rotors and butterfly type rotors) |
|
Material: |
SS304/SS316 |
|
Seal Material: |
CHINAMFG (Standard, approval) |
|
Max. Flow: |
43000Liter/h |
|
Max.pressure: |
10bar |
|
Speed |
1-1000 rmp |
|
Rotor Type: |
2-leaves, 3-leaves, butterfly, signal butterfly |
|
Mechanical seal: |
SIC/SiC/EPDM(Standard) |
|
Motor power: |
0.75kw, 1.1kw, 1.5kw, 2.2kw, 3kw, …22KW |
|
Sealing option: |
Sanitary single mechanical seal/Double mechanical seal with cooling system |
|
Voltage: |
220V, 380V(110-480v) |
|
Motor: |
ABB, Siemens,Our Domestic Brand,50hz/ 60hz |
|
Surface treatment: |
Inner polished and Sandblast outside |
|
connection: |
Clamp, Thread, weld, Flange |
|
Availably standard: |
DIN, SMS, 3A, RJT, ISO/IDF |
|
Operated: |
Electic |
|
Application scope: |
Dairy, food, beverage, pharmacy, cosmetic, etc |
|
Packaging Details: |
Plywood case |
|
Delivery details: |
Usually within1-7 days after receiving T/T down payment |
|
We can customize the Lobe Pump according to customer requirements. |
|
|
Technical Parameters |
||||
|
Model |
Capacity/Per centum rotate (L) |
Speed(RPM) |
Flow(L/H) |
Power(KW) |
|
ACE-3R |
3L |
100-500 |
300-800 |
0.55 |
|
ACE-6R |
6L |
100-500 |
650-1600 |
0.75 |
|
ACE-8R |
8L |
100-500 |
850-2160 |
1.5 |
|
ACE-12R |
12L |
100-500 |
1300-3200 |
2.2 |
|
ACE-20R |
20L |
100-500 |
2100-5400 |
3 |
|
ACE-30R |
30L |
100-500 |
3200-6400 |
4 |
|
ACE-36R |
36L |
100-500 |
3800-7600 |
4 |
|
ACE-52R |
52L |
100-500 |
5600-11000 |
5.5 |
|
ACE-66R |
66L |
100-500 |
7100-14000 |
7.5 |
|
ACE-78R |
78L |
100-500 |
9000-18000 |
7.5 |
|
ACE-100R |
100L |
100-500 |
11000-22000 |
11 |
|
ACE-135R |
135L |
100-500 |
15000-30000 |
15 |
|
ACE-160R |
160L |
100-500 |
17000-34000 |
18.5 |
|
ACE-200R |
200L |
100-500 |
21600-43000 |
22 |
Detailed Photos
Packaging & Shipping
Other pumps
Certifications
FAQ
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in plywood case or carton package for small parts.
If you have legally registered patent, we can pack the goods in your branded boxes after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T in advance, 30% as deposit, and finish 70% balance payment before delivery.
We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages before you pay the balance.
Q3. What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB, CIF, DDU.
Q4. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 3 to 4 weeks after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends
on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q5. Can you produce according to the samples?
A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings.
Q6.Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
Q7: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A:1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them, no matter where they come from.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Video Technical Support, Online Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 2 Years |
| Mesh Form: | External Engaged |
| Tooth Flank: | Stainless Steel Rotary Lobe |
| Tooth Curve: | Stainless Steel Rotary Lobe |
| Power: | Electric |
| Samples: |
US$ 850/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How Are Roots Vacuum Pumps Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
Roots vacuum pumps play a significant role in various applications within the automotive industry. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Brake System Vacuum Pumps:
– Vacuum Boosters: Roots vacuum pumps are commonly used as vacuum boosters in automotive brake systems. They assist in enhancing the braking performance by providing the necessary vacuum for power brake operation. When the driver applies the brake pedal, the vacuum booster uses the suction power generated by the Roots pump to amplify the force applied to the brake master cylinder, resulting in more effective braking.
– Electric Brake Vacuum Pumps: In modern electric or hybrid vehicles, where traditional engine-driven vacuum sources may not be available, electric brake vacuum pumps are utilized. These pumps, often based on the Roots principle, generate vacuum independently to power the brake booster and ensure reliable braking performance.
2. Emissions Control:
– Evaporative Emission Control: Roots vacuum pumps are employed in evaporative emission control systems to prevent the release of harmful vapors from the fuel system into the atmosphere. These pumps create a vacuum within the system, purging and storing fuel vapors in a canister for subsequent combustion or recycling.
– Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV): PCV systems, which are designed to reduce emissions and maintain the integrity of the engine, also utilize Roots vacuum pumps. These pumps draw crankcase gases and vapors, including oil mist, from the engine’s crankcase into the intake manifold for combustion, improving overall engine efficiency and reducing pollution.
3. Engine Testing and Development:
– Vacuum Leakage Testing: Roots vacuum pumps are utilized for vacuum leakage testing in engine manufacturing and development. By creating a vacuum in the intake manifold or other engine components, these pumps enable the detection of leaks and ensure the integrity of the engine’s air delivery system.
– Air Flow Calibration: During engine testing and calibration, Roots vacuum pumps are used to simulate various operating conditions by controlling the intake air flow. This allows engineers to fine-tune the engine’s performance, optimize fuel-air mixture ratios, and assess the engine’s efficiency and emissions characteristics.
4. HVAC Systems:
– Climate Control: Roots vacuum pumps are employed in automotive HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems to facilitate the flow and distribution of air. These pumps help regulate the operation of HVAC components, such as air blend doors and vacuum actuators, ensuring proper air temperature and direction control inside the vehicle cabin.
5. Fuel System and Turbocharging:
– Fuel Transfer and Evacuation: In automotive fuel systems, Roots vacuum pumps are used for fuel transfer and evacuation. These pumps assist in priming the fuel system, removing air pockets, and ensuring the continuous flow of fuel to the engine, enhancing the overall fuel delivery performance.
– Turbocharger Control: Roots vacuum pumps are sometimes employed in turbocharged engines to control the actuation of variable geometry turbochargers (VGT). These pumps provide the necessary vacuum signals to actuate the VGT mechanism, optimizing turbocharger performance and enhancing engine efficiency.
6. Other Applications:
– Electric Vehicle Battery Systems: In electric vehicles, Roots vacuum pumps are utilized to create a vacuum in battery enclosures, helping to maintain the integrity and safety of the battery system by preventing the ingress of moisture, dust, or contaminants.
– Engine Air Induction: Some automotive engines utilize Roots-type superchargers or twin-screw superchargers, which are essentially positive displacement Roots vacuum pumps operating in reverse. These devices compress and force air into the engine’s intake manifold, resulting in increased engine power and performance.
In summary, Roots vacuum pumps find extensive utilization in the automotive industry. They play a crucial role in brake systems, emissions control, engine testing and development, HVAC systems, fuel systems, turbocharging, electric vehicle battery systems, and engine air induction. By contributing to braking performance, emissions reduction, engine calibration, HVAC functionality, fuel system efficiency, turbocharger control, battery system safety, and engine power enhancement, Roots vacuum pumps contribute significantly to the overall operation and performance of automotive systems and components.
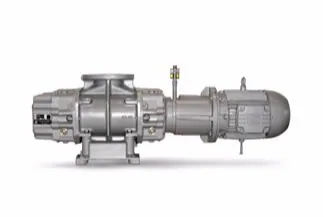
What Is a Roots Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A Roots vacuum pump, also known as a Roots blower or a rotary lobe pump, is a type of positive displacement vacuum pump that is widely used for various industrial applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a Roots vacuum pump is and how it works:
A Roots vacuum pump consists of two synchronized rotors, known as lobes or impellers, that rotate in opposite directions within a housing. The lobes have a unique helical shape with multiple lobes, which allows them to trap and move gas efficiently. The rotors are synchronized with the help of timing gears to maintain precise clearances between the lobes and the housing.
The operation of a Roots vacuum pump can be described in the following steps:
1. Inlet Stage: The process begins with the lobes rotating in opposite directions. As the lobes rotate, the volume between them and the housing gradually increases, creating a larger space at the inlet side of the pump. This expansion of the volume causes the gas to enter the pump through the inlet port. The gas is drawn in due to the pressure difference between the inlet and the pump’s internal chamber.
2. Compression Stage: As the gas enters the pump, it gets trapped in the spaces between the lobes and the housing. As the lobes continue to rotate, the trapped gas gets carried along the rotating lobes. The gas is essentially trapped in the pockets formed by the lobes and the housing. The rotating lobes then compress the gas as they move towards the outlet side of the pump.
3. Outlet Stage: As the lobes approach the outlet side of the pump, the volume between them and the housing decreases, resulting in the compression of the trapped gas. This compression raises the pressure of the gas, causing it to be expelled through the outlet port of the pump. The expelled gas is then discharged into the atmosphere or directed to a downstream process or another vacuum pump, depending on the application.
It’s important to note that a Roots vacuum pump operates as a non-contacting pump, meaning that there is no physical contact between the lobes or between the lobes and the housing. This characteristic eliminates the need for lubrication within the pump and reduces the risk of contamination or oil vapor backstreaming into the vacuum system.
Roots vacuum pumps are known for their high pumping speed and ability to handle large volumes of gas. However, they are not capable of achieving high vacuum levels on their own. To achieve higher vacuum levels, a Roots pump is often used in conjunction with other vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps or diffusion pumps, in a hybrid or combination pumping system.
In summary, a Roots vacuum pump operates based on the principle of positive displacement. It utilizes synchronized rotating lobes to trap and compress gas, allowing it to be discharged at a higher pressure. The non-contacting design of the pump eliminates the need for lubrication and reduces the risk of contamination. Roots vacuum pumps are commonly employed in various industrial applications, especially when high pumping speed and large gas handling capacity are required.


editor by CX 2024-03-23
China supplier Cast Iron Diaphragm Hydraulic Vacuum Centrifugal Oil Gear Pneumatic Price Water Pump with Great quality
Merchandise Description
Cast Iron Diaphragm Hydraulic Vacuum Centrifugal Oil Gear Pneumatic Value Drinking water Pump
Solution Description
Hand oil pump
Force:1.5Mpa-2Mpa
Vol.:.6Kg
Outlet:M8x1
Hand oil pump
Stress:1.5Mpa-2Mpa
Vol.:.4Kg
Outlet:M8x1
2L oil lubrication pump
Stress:2.5Mpa
Viscosity:#twenty-#320
Voltage:24V/220V
Power:20W
Reservoir:2L
3L oil lubrication pump
Pressure:2.5Mpa
Viscosity:#twenty-#320
Voltage:24V/220V
Electrical power:20W
Reservoir:3L
4L oil lubrication pump
Strain:2.5Mpa
Viscosity:#twenty-#320
Voltage:24V/220V
Electrical power:20W
Reservoir:4L
6L oil lubrication pump
Strain:2.5Mpa
Viscosity:#twenty-#320
Voltage:220V/380V
Energy:60W
Reservoir:6L
DLX-Injectors
Discharge:.571ml/cyc-.06ml/cyc-.1ml/cyc-.2ml/cyc-.3ml/cyc-.4ml/cyc-.5ml/cyc
Inlet:M8/M10/Pt1/8
Outlet:M8
Metering Device
The slowest:#-Quickest #5
6kg electric powered lubrication oil pump and lubrication station
Relevant Item
Emitech could provide all of the recent central lubrication technique and its components at the great price.
6kg Oil Pump for lubrication the CNC Program
FAQ
Q: How to purchase?
A: You should send out me the inquiry about what’s kind of equipment you want to lubricate, and our crew can give you with the complete parts. Following the list is verified, we will update the air price or the sea price for you to assess.
Q: How about the foremost time?
A: We normally have sufficient in stock and usually no later than 2 weeks, we could launch them.
Q.Payment
A: T/T,WesternUnion,LC
Q.Transportation
A: Transported by DHL,UPS,EMS,Fedex ,Air freight, Sea.
Q: Does Emitech can provide samples?
A: Sure, of program.
What Are Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps use air flow as the source of energy. The system is ideal for dewatering wet media, creating filter cakes, and pneumatically moving materials through a pipe. A vacuum pump works through air flow that is moved by differential pressure. The pump’s air flow develops a vacuum in a chamber that is called the vacuum box. As the air flow collects gas at a faster rate than atmospheric pressure, it is considered the “heart” of a vacuum system.
Principles of operation
Vacuum pumps work by reducing the volume of air that moves through them. Depending on the design, there are several different types of vacuum pumps. All of these types operate under the same principles, but have their own special features. Here are some of their most important characteristics. In addition to their capacity, the main differences between these pumps are their manufacturing tolerances, materials of construction, and level of tolerance for chemicals, oil vapor, and vibration.
Vacuum pumps create a partial or low-pressure vacuum by forcing gas molecules from their high-pressure states to their low-pressure states. However, these pumps can only achieve a partial vacuum, and other methods are necessary to reach a higher level of vacuum. As with all pumps, there are several ways to increase the level of a vacuum.
First, consider the type of vacuum you want. This is the most important factor when choosing a vacuum pump. If you need a high level of vacuum, you’ll need a high-quality vacuum pump. High-quality vacuum pumps have a high pressure limit, while ultrahigh-quality pumps are capable of achieving a very low vacuum. As the pressure decreases, the amount of molecules per cubic centimeter decreases and the quality of the vacuum increases.
Positive displacement pumps are best suited for low and medium-pressure systems. But they can’t reach high vacuum, which is why most high-pressure systems use two pumps in tandem. In this case, the positive displacement pump would stall and the other one would be used instead. Similarly, entrapment pumps have higher-pressure limits, so they must be refreshed frequently or exhaust frequently when there is too much gas to capture.
Another important aspect of vacuum pump operation is its speed. The speed of pumping is proportional to the differential pressure across the system. Therefore, the faster the pumping speed, the lower the draining time.
Design
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to generate a vacuum. It can create a low or high vacuum. These pumps are used in the process of oil regeneration and re-refining. The design of a vacuum pump must be compatible with the vacuum. The pump’s mass and speed should be matched.
The design of a vacuum pump is important for many reasons. It should be easy to use and maintain. Vacuum pumps need to be protected from external contamination. For this reason, the oil must be kept clean at all times. Contamination may damage the oil, resulting in pump failure. The pump’s design should include features that will prevent this from happening.
The main objective of a vacuum pump is to remove air and other gases from a chamber. As the pressure of the chamber drops, the amount of molecules that can be removed becomes more difficult. Because of this, industrial and research vacuum systems typically require pumps to operate over a large pressure range. The range is generally between one and 10-6 Torr. A standard vacuum system uses multiple pumps, each covering a portion of the pressure range. These pumps can also be operated in a series to achieve optimal performance.
The design of a vacuum pump can vary depending on the application and the pressure requirement. It should be sized appropriately to ensure that it works properly. There are several different types of pumps, so selecting the right pump is essential to maximizing its efficiency. For example, a slow running vee belt drive rotary vane vacuum pump will have a lower running temperature than a fast-running direct-drive pump.
Performance
The performance of a vacuum pump is an important indicator of its overall condition. It helps determine whether the system is performing optimally and how high the ultimate vacuum level can be achieved. A performance log should be maintained to document variations in pump operating hours and voltage as well as the temperature of the pump’s cooling water and oil. The log should also record any problems with the pump.
There are several ways to increase the performance of a vacuum pump. For example, one way is to decrease the temperature of the working fluid. If the temperature of the fluid is too high, it will lead to a low vacuum. A high temperature will make the vacuum degree of the pump even lower, so heat transfer is an important part of the process.
Nozzles are another major component that impacts the performance of a vacuum pump. Damage or clogging can result in a compromised pumping capacity. These problems can occur due to a number of causes, including excessive noise, leakage, and misassembled parts. Nozzles can also become clogged due to rusting, corrosion, or excess water.
Performance of vacuum pump technology is vital for many industries. It is an integral part of many central production processes. However, it comes with certain expenses, including machines, installations, energy, and maintenance. This makes it essential to understand what to look for when purchasing a vacuum pump. It is important to understand the factors that can influence these factors, as they affect the efficiency of a vacuum pump.
Another important factor in determining the performance of a vacuum pump is throughput. Throughput is a measurement of how many molecules can be pumped per unit of time at a constant temperature. Moreover, throughput can also be used to evaluate volume leak rates and pressure at the vacuum side. In this way, the efficiency of a vacuum pump can be judged by the speed and throughput of its leaks.
Atmospheric pressure
Vacuum pumps work by sucking liquids or air into a container. The amount of vacuum a pump can create is measured in pressure units called atms (atmospheric pressure). The pressure of a vacuum pump is equal to the difference between atmospheric pressure and the pressure in the system.
The amount of force produced by air molecules on each other is proportional to the number of impacts. Therefore, the greater the impact, the higher the pressure. In addition, all molecules have the same amount of energy at any temperature. This holds true for both pure and mixture gases. However, lighter molecules will move faster than heavier ones. Nevertheless, the transfer of energy is the same for both.
The difference between atmospheric and gauge pressure is not always straightforward. Some applications use one term to describe the other. While the two concepts are closely related, there are key differences. In most cases, atmospheric pressure is a higher number than gauge pressure. As a result, it can be confusing when choosing a vacuum pump.
One method is to use a U-tube manometer, a compact device that measures the difference between atmospheric pressure and vacuum. This device is commonly used for monitoring vacuum systems. It can measure both negative and positive pressure. In addition, it uses an electronic version of a gauge.
The atmospheric pressure affects the performance of a vacuum pump. When working with porous materials, the pump must overcome leakage. As a result, it must be equipped with enough capacity to compensate for variations in the porosity of the work piece. This is why it is critical to buy a vacuum pump that has a large enough capacity to handle the variation.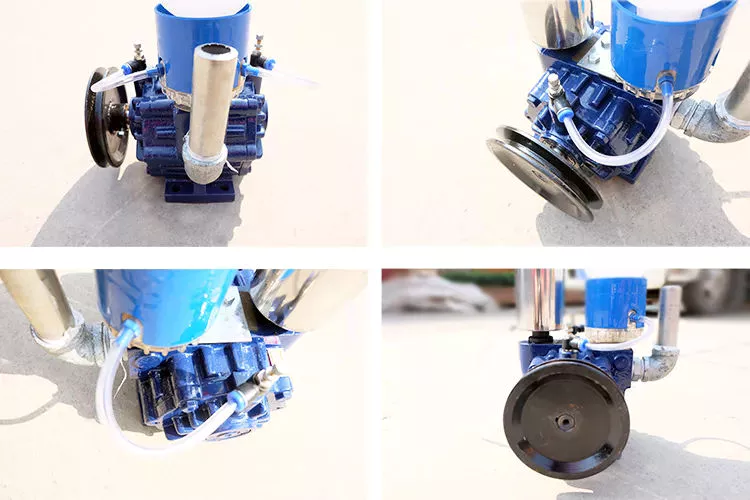
Typical application
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of applications. They generate low and high pressures and are used to evaporate water or gases from various materials. They are also used in petroleum regeneration and re-refining processes. Typical applications of vacuum pumps include: a.
b. Rotary vane pumps are used in a variety of vacuum applications. They are suitable for industrial applications, freeze drying and cabinet making. They use oil as a sealant and coolant, allowing them to perform well in a variety of applications. This makes them ideal for use in a variety of industries.
The pumping rate of the vacuum pump is important. This refers to the volume pumped from a given point at a given rate. The higher the speed, the faster the pump will expel the air. Depending on the gas composition, this number will vary. When choosing a vacuum pump, gas composition and process requirements should be considered.
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industries from laboratories to medical facilities. In medical applications, they are used in radiation therapy and radiopharmaceuticals. They are also used in mass spectrometers, which are instruments used to analyze solid, liquid, or surface materials. Vacuum pumps are also used in decorative vacuum coatings and Formula 1 engine components. A trash compactor is another example of using a vacuum pump.
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of applications including water purification and aeration. Vacuum pumps are also used in portable dental equipment and compressors in the dental industry. Vacuum pumps are also used in molds for dental implants. Other common applications for vacuum pumps include soil aeration and air sampling.


High Pressure 4140 Steel Oil Pump Gear Shaft

Substantial force 4140 steel oil pump equipment shaft
Area: As your necessity
Content: Steel / aluminum / brass / iron / zinc / alloy
Any other materials and dimension depends on customers’ need.
Use: CZPTry / furniture / toy / woodboard / wall
Euipment: CNC machine
Tests tools: Projector
| Content | CZPT steel, copper, brass, carbon steel, aluminum (according to customer’s requirement. |
| Surface Treatment | Zn-plating, Ni-plating, Cr-plating, Tin-plating, copper-plating, the wreath oxygen resin spraying, the heat disposing, very hot-dip galvanizing, black oxide coating, painting, powdering, color zinc-plated, blue black zinc-plated, rust preventive oil, titanium alloy galvanized, silver plating, plastic, electroplating, anodizing etc. |
| Main CZPT | CZPT screw,bolt, nuts,fastener,knob,pins, bushing, sleeve,gear, stamping parts,washer,gasket,plastic molding injection parts,standoff,CNC machining service,accessories etc. |
| Producing CZPT | CNC machine , automatic lathe machine,stamping machine,CNC milling machine,rolling machine,lasering,tag grinding machine etc. |
| Management System | ISO9001 – 2008 |
| Available Certificate | RoHS, SGS, Material Certification |
| Testing CZPT | Projecting apparatus, Salt Spray Test, Durometer, and Coating thickness tester , 2D projector |
| Lead time | ten-15 working days as usual,It will based on the detailed order quantity. |
| Managing Returned Goods | With quality problem or deviation from drawings |
| Delivery of Samples | By DHL,Fedex,UPS, TNT,EMS^^ |
| Warranty | Replacement at all our cost for rejected products |
| Main Markets | North CZPTica, South CZPTica, CZPTern CZPTe , West CZPTe , North CZPTe, South CZPTe, Asia |
| How to order | * You send us drawing or sample |
| * We carry through project assessment | |
| * We give you our design for your confirmation | |
| * We make the sample and send it to you after you confirmed our design | |
| * You confirm the sample then place an order and pay us 30% deposit | |
| * We start producing | |
| * When the goods is done, you pay us the balance after you confirmed pictures or tracking numbers. | |
| * CZPT is done, thank you!! | |
| Purposes | Toy,CZPT, instrument, electrical equipment, household appliances, furniture, mechanical equipment, daily living equipment, electronic sports equipment, light industry products, sanitation machinery, market/ hotel equipment supplies, artware etc. |

Japan Nissan Forklift Diesel Oil Gear Fuel Pump Parts 17010-50K60

CZPT CZPT Diesel Motor:
- Cummins motor and spare parts
- Deutz engine and spare areas
- JAPAN ISUZU C240PKJ/4JG2/6BG1
- JAPAN Mitsubishi S4S/S6S
- italay KOHLER
China CZPT Manufacturer Diesel Motor:
- YTO engine and spare components
- Weichai motor and spare components
- ShangChai motor and spare parts
- Yuchai motor and spare areas
- CZPT engine and spare components
- Chaochai engine and spare areas
- Dachai engine and spare parts
- FAW (CZPT) engine and spare areas
- Changchai motor and spare parts
- Yunei motor and spare components
- Laidong motor and spare components
- CZPTa engine and spare components
- Quanchai engine and spare elements
- Xihu (West Lake) Dis. motor and spare components
Make sure you feel totally free to send out inquiry to us for far more information of this merchandise or other products in our showroom.

Big Sale Gear Motor DC 12V High Torque for Peristaltic Pump

Merchandise no:PG28395124500-126K
Voltage:12V
Rated load pace:thirty.2rpm
Rated load torque:7.8kgf.cm
No load speed:35.7rpm
| Simple data | |
| Solution identify | PG28395124500-126K |
| Motor kind | carbon-brush commutator |
| Equipment kind | Straight gearwheel,planet building |
| Housing material | Steel |
| Geartrain materials | Steel and Powdered Metallic,POM optional |
| Bearing at output shaft | Ball bearing |
| CZPT | Grease for large-minimal temperature, -sixty two—+204 degree |
| Backlash at no-load | <1°,MIN0.3° |
| OEM & ODM Provider | Available |
| Certification | CE,ROHS,ISO/TS16949 |
| An precise model of gearbox and motor blend | |
| Item seires | P28 series |
| An specific Model NO. | PG28395124500-126K |
| Motor Voltage(VDC) | 12 |
| Motor no load speed(rpm) | 4500 |
| Gearbox reduction ratio | 126 |
| Gearmotor no load present(A) | <1.200 |
| Gearmotor no load speed(rpm) | 35.seven+/-10% |
| Gearmotor rated load torque(kgf.cm) | seven.eight |
| Gearmotor rated recent(A) | <6.500 |
| Gearmotor rated load speed(rpm) | 35.seven+/-ten% |
| Sound (DB) | <60DB |
| Life time | 1000+ hours (varies by software) |
| Rotation | CW/CCW reversible |
WORKSHOP:
WAREHOUSE:
Transportation:
CERTIFICATION:
Group:
FAQ:
Q:1.What variety of motors you can give?
A: For now, we largely offer planetary gear box dc motors (including brush and brushless) with diameter selection in sixteen~60mm and also Dia10~80mm size gear motors.
Q:2. Can you deliver me a price checklist?
A: For all of our motors, they are CZPT dependent on diverse requirements like life span, sound, voltage, and shaft etc. The cost also may differ in accordance to annual quantity. So it’s really tough for us to give a price record. If you can share your detailed specifications and yearly quantity, we will see what supply we can offer.
Q:three. What is the lead time for typical order?
A: For orders, the CZPT guide time is thirty-35 times and this time can be shorter or longer based on various design, interval and quantity.
Q:four. Is it possible for you to build new motors if we can give tooling expense?
A: Yes. Please kindly share the comprehensive requirements like efficiency, dimension, once-a-year amount, goal price and so forth. Then we will make our analysis to see if we can organize or not.
Q:5. Can I get some samples?
A: It depends. If only a few samples for private use or substitute, I am concerned it will be tough for us to give due to the fact all of our motors are personalized manufactured and no stock available if there is no even more demands. If just sample screening ahead of the official purchase and our MOQ, cost and other phrases are appropriate, we might enjoy to supply samples.

Cast Iron Castings, Pump Casting, Gear Castings

Firm INTRODUCTION
HangZhou Doushan CZPTry CZPT Co.,Ltd has been specialized in castings for numerous a long time. Annual generation capability can achieve much more than 500000 ton. Our products mainly products include EN545 12842 ductile iron pipe fittings Formwork areas Flat anchor for Personal computer Strand Valve and pump human body others by drawings. Now our merchandise are export to a lot of countries, such us France, Spain, Morocco, UAE,
South Africa, Southe Korea, Vitenam and so so.
Creation DESCRIPTION
| Substance | Ductile Iron/Gray Iron |
| Dimensions | DN40mm–DN1000mm(as your call for) |
| Procedure | Resin Sand/Clay Sand/Coated Sand |
| Surface area Treatment | Polish/Sand Blast/Spray Paint |
Bundle AND Cargo

Motor Oil Pump, Gear Pump Food, Electric Oil Pump High-Pressure

Summarize:
1. KCB CZPTtric CZPT Equipment Oil Pump Transfer Squander Oil, Olive Oil, Crude Oil, Diesel Oil is designed for pumping gentle gas oils these kinds of as diesel, kerosene, and biodiesel. It is also feasible to pump vegetable oil, motor oil, and even glycerol.
two. It is helical gear pump, and developed-in by-go valve. For pumping cleanse viscous liquids, not made up of abrasive or solid particles.
three. They can operate dry for only intermediate amounts of time, allowing for the use of a suction hose for collecting fluids from a tank. They should not be operate dry for an extended time period of time as oil is necessary to lubricate the pump head.
CZPTly used in:
- CZPTs: Pure or filled biHangZhou, pitch, diesel oil, crude oil, lube oil and many others.
- CZPTs: Sodium silicate, acids, plastics, combined chemical compounds, isocyanates and so on.
- Paint and ink.
- Resins and adhesives.
- Pulp and paper: acid, cleaning soap, lye, black liquor, kaolin, lime, latex, sludge etc.
- Foodstuff: Chocolate, cacao butter, fillers, sugar, vegetable fat and oils, molasses, animal foods etc
Item information:
| Functioning Theory: | Double Gears |
| Pump human body materials: | Forged Iron, SS304, SS316 |
| Gear material: | #forty five Steel, Copper, SS304, SS316 |
| Temperature range: | Normal ≤ 70 C, Special ≤ three hundred C |
| CZPTr: | Motor engine, diesel motor |
| Electricity specs: | 220V, 240V, 380V, 400V, 415V, 440V, 460V, 50hz/60hz |
| Max circulation price: | 9600 L/min |
| Max discharge stress: | 1.45MPa |
| Type of connection: | Quick couple, Thread, Flange |
| Shaft seal type: | Oil seal, CZPT seal, CZPT seal |
| Sliding bearing: | Great aseismic performance |
| Helical Gear: | Good meshing functionality, steady transmisson of gear reduce sound. |
Performance Knowledge:
| Model | Flow rate | Max Pressure | Max Power | Inlet&Outlet |
| (L/m) | (Mpa) | (kW) | (mm) | |
| KCB18.three | eighteen.three | 1.forty five | 1.5 | 20 |
| KCB33.three | 33.3 | one.45 | 2.2 | 20 |
| KCB55 | 55 | 1 | 3 | 25 |
| KCB83.three | eighty three.3 | one | 4 | 40 |
| KCB133 | 133 | 1 | 5.5 | 50 |
| KCB200 | 200 | 1 | 7.five | 50 |
| KCB300 | 300 | 1 | 11 | 80 |
| KCB483.three | 483.3 | one | 11 | 80 |
| KCB633 | 633 | .8 | 22 | a hundred |
| KCB960 | 960 | .6 | 30 | 100 |
| KCB1200 | 1200 | .6 | 37 | 150 |
Company information:
ZHangZhoug CZPT CZPT Co., Ltd is one of the top companies and exporters in the discipline of industry pumps with manufacturing amenities in mainland China. We are specialised in oil pump, diaphragm pump, diesel engine pump, centrifugal pump, screw pump, chemical pump and so forth.
